3.1.5.1. Steel01 Material
This command is used to construct a uniaxial bilinear steel material object with kinematic hardening and optional isotropic hardening described by a non-linear evolution equation (REF: Fedeas).
- uniaxialMaterial Steel01 $matTag $Fy $E0 $b <$a1 $a2 $a3 $a4>
Argument |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
$matTag |
integer |
integer tag identifying material |
$Fy |
float |
yield strength |
$E0 |
float |
initial elastic tangent |
$b |
float |
strain-hardening ratio (ratio between post-yield tangent and initial elastic tangent) |
$a1 |
float |
optional: isotropic hardening parameter: increase of compression yield envelope as proportion of yield strength after a plastic strain of $a2*($Fy/E0). |
$a2 |
float |
optional:isotropic hardening parameter (see explanation under $a1) |
$a3 |
float |
optional: isotropic hardening parameter: increase of tension yield envelope as proportion of yield strength after a plastic strain of $a4*($Fy/E0) |
$a4 |
float |
optional: isotropic hardening parameter (see explanation under $a3) |
Note
By default there is no isotropic hardening.
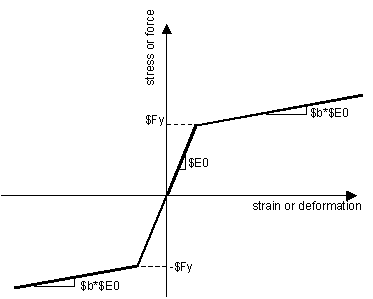
Fig. 3.1.5.1 Steel01
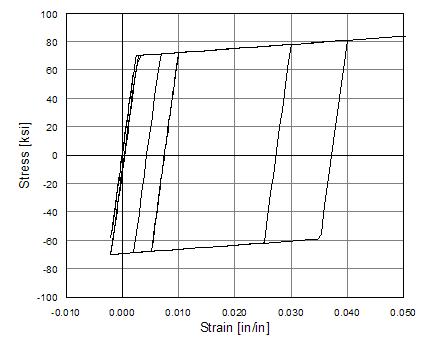
Fig. 3.1.5.2 Steel01 Material – Default Hysteretic Behavior (NO isotropic hardening)
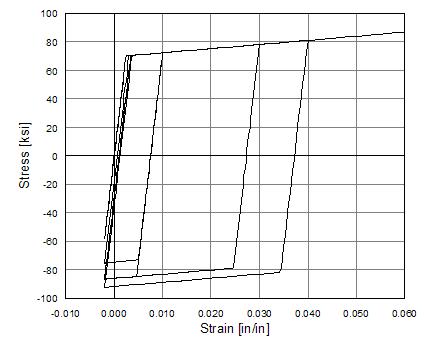
Fig. 3.1.5.3 Steel01 Material – Hysteretic Behavior of Model with Isotropic Hardening in Compression
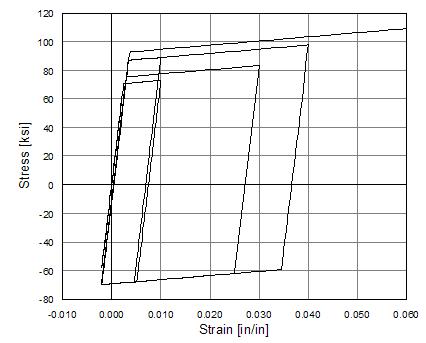
Fig. 3.1.5.4 Steel01 Material – Hysteretic Behavior of Model with Isotropic Hardening in Tension
Example
The following is used to construct a Steel01 mataerial with a tag of 1, a yield strength of $60.0** and an initial tangent stiffness of 30000,0.
Tcl Code
uniaxialMaterial Steel01 60.0 30000.0
Python Code
uniaxialMaterial('Steel01',60.0,30000.0)
Code Developed by: Michael H. Scott