3.1.10.19. MEFI Element
The Membrane Fiber (MEFI) element, is described by four nodes, each containing three degrees of freedom (DOFs), two translations, and one in-plane rotation (drilling) DOF, which incorporates a blended interpolation function for the displacements over the element. The element formulation accommodates the quadrature points and weights of the classical finite element formulation of membrane elements to resemble strips (fibers), similarly to macroscopic elements.
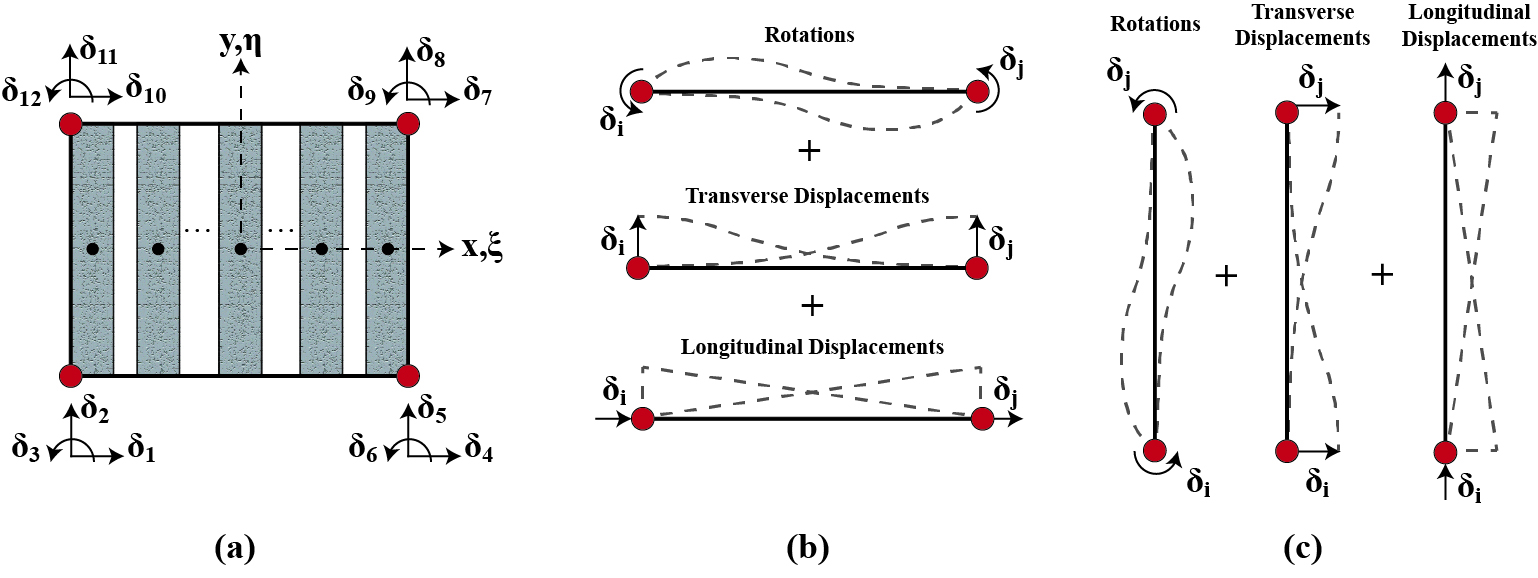
Fig. 3.1.10.18 MEFI Element: (a) Element idealization; (b) Interpolation function at bottom and top edges; (c) Interpolation function at left and right edges.
This command is used to construct a MEFI element object.
Command
element MEFI $eleTag $iNode $jNode $kNode $lNode $numFib -width $widths -sec $secTags
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
$eleTag |
integer |
unique element object tag |
$iNode $jNode $kNode $lNode |
4 integer |
tags of element nodes defined in counterclockwise direction |
$numFib |
integer |
number of element macro-fibers |
$widths |
list float |
a list of numFib macro-fiber widths |
$secTags |
list int |
a list of numFib macro-fiber section tags |
The following recorders are available with the MEFI element.
Recorder |
Description |
|---|---|
forces |
element global forces |
stresses |
element stresses |
strains |
element strains |
RCPanel $fibTag $Response |
returns material $Response for a $fibTag-th panel (1 ≤ fibTag ≤ numFib). For available $Response(s) refer to material |
Notes
Command Example
The following example constructs a MEFI element with tag 1 between nodes 1, 2, 3, 4, with 8 macro-fibers. Each macro-fiber has width 1 and material tag 1.
Tcl Code
element MEFI 1 1 2 3 4 8 -width 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 -sec 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1;
Python Code
element('MEFI', 1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, '-width', 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, '-sec', 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1)
Pushover Example
The following example creates a pushover analysis for a reinforced concrete wall. The example is based on specimen RW-A20-P10-S38 tested by Tran and Wallace (2012).
Tcl Code
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Description: Pushover analysis of specimen RW-A20-P10-S38 (Tran and Wallace, 2012)
# Created by: Carlos López Olea (carloslopezolea@gmail.com)
# Last Modification: 01/2024
# Basic units: N, mm, sec
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Start of model generation
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
wipe
model Basic -ndm 2 -ndf 3
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Set geometry, nodes, boundary conditions
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Nodes for RC wall
for {set i 1} {$i <= 8} {incr i} {
node [expr 2*$i-1] 0.0 [expr (2209.8/7)*($i-1)]
node [expr 2*$i] 1220.0 [expr (2209.8/7)*($i-1)]
}
# Nodes for loading transfer beam
for {set i 9} {$i <= 10} {incr i} {
node [expr 2*$i-1] 0.0 [expr 2209.8 + (457.2/2)*($i-8)]
node [expr 2*$i] 1220.0 [expr 2209.8 + (457.2/2)*($i-8)]
}
# Restraint fixes
fix 1 1 1 1
fix 2 1 1 1
# Node restraints
equalDOF 15 16 1
equalDOF 17 18 1
equalDOF 19 20 1
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Define and build materials
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Build uniaxial steel materials
uniaxialMaterial Steel02 1 469.93 200000.0 0.02 20.0 0.925 0.15; # steel X
uniaxialMaterial Steel02 2 409.71 200000.0 0.02 20.0 0.925 0.15; # steel Y web
uniaxialMaterial Steel02 3 429.78 200000.0 0.01 20.0 0.925 0.15; # steel Y boundary
# Build uniaxial concrete materials
uniaxialMaterial Concrete02 4 -47.09 -0.00232 0.0 -0.037 0.1 2.13 1738.33; # unconfined concrete
uniaxialMaterial Concrete02 5 -53.78 -0.00397 -9.42 -0.047 0.1 2.13 1827.12; # confined concrete
# Build nD concrete materials
nDMaterial OrthotropicRAConcrete 6 4 0.00008 -0.00232 0.0 -damageCte1 0.175 -damageCte2 0.5; # unconfined concrete
nDMaterial OrthotropicRAConcrete 7 5 0.00008 -0.00397 0.0 -damageCte1 0.175 -damageCte2 0.5; # confined concrete
# Build nD steel materials
nDMaterial SmearedSteelDoubleLayer 8 1 2 0.0027 0.0027 0.0; # steel web
nDMaterial SmearedSteelDoubleLayer 9 1 3 0.0082 0.0323 0.0; # steel boundary
# Build reinforced concrete sections
section RCLMS 10 1 1 -reinfSteel 8 -conc 6 -concThick 152.4; # wall web
section RCLMS 11 1 2 -reinfSteel 9 -conc 6 7 -concThick 50.8 101.6; # wall boundary
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Define and build elements
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Build MEFI elements
set numFib 8; # number of element macro-fibers
set db 228.6; # boundary length discretization
set dw 127.133; # web length discretization
for {set i 1} {$i <= 9} {incr i} {
element MEFI $i [expr 2*$i-1] [expr 2*$i] [expr 2*$i+2] [expr 2*$i+1] $numFib -width $db $dw $dw $dw $dw $dw $dw $db -sec 11 10 10 10 10 10 10 11;
}
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Define recorders
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
recorder Element -file MEFI/MEFI1_forces.out -time -ele 1 forces
recorder Element -file MEFI/MEFI1_stresses.out -time -ele 1 stresses
recorder Element -file MEFI/MEFI1_strains.out -time -ele 1 strains
recorder Element -file MEFI/MEFI1_fiber1_strain.out -time -ele 1 RCPanel 1 panel_strain
recorder Element -file MEFI/MEFI1_fiber1_stress.out -time -ele 1 RCPanel 1 panel_stress
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Gravity load analysis
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Define gravity load pattern
pattern Plain 1 Linear {
load 19 0.0 -320272.0 0.0
load 20 0.0 -320272.0 0.0
}
# Analysis generation
system BandGeneral
constraints Transformation
numberer RCM
test NormUnbalance 100.0 100 0
algorithm Newton
integrator LoadControl 0.05
analysis Static
set ok [analyze 20]
if {$ok == 0} {
puts "Gravity analysis completed successfully";
} else {
error "Gravity analysis failed";
}
loadConst -time 0.0
wipeAnalysis
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Lateral load analysis
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Define lateral load pattern
pattern Plain 2 Linear {
load 15 1000.0 0.0 0.0
load 17 1000.0 0.0 0.0
load 19 1000.0 0.0 0.0
}
# Analysis generation
system BandGeneral
constraints Transformation
numberer RCM
test NormDispIncr 0.001 100 0
algorithm Newton
integrator DisplacementControl 17 1 0.1
analysis Static
set ok [analyze 800]
if {$ok == 0} {
puts "Pushover analysis completed successfully";
} else {
error "Pushover analysis failed";
}
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Perform tests
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Base shear test
reactions
set BSref 421968.7; # reference value for base shear
set BS [expr abs([nodeReaction 1 1] + [nodeReaction 2 1])]; # computed value for base shear
set BSerr [expr abs($BS-$BSref)/$BSref]; # compute relative error
puts "Relative base shear error is abs(BS-BSref)/BSref: $BSerr"
if {$BSerr <= 0.0001} {
puts "Base shear test completed successfully";
} else {
error "Base shear test failed";
}
REFERENCES:
López, C. N., Rojas, F., & Massone, L. M. (2022). Membrane fiber element for reinforced concrete walls – the benefits of macro and micro modeling approaches. Engineering Structures, 254, 113819. (link).
Code Developed by: C. N. López